Page Contents
GST Audit and GST Audit Checklist
In this article, we have discussed the points to be checked in GST Audit and later we have provided a GST Audit checklist.
A taxpayer registered under GST will undergo GST Audit which would involve examination of GST returns, documents, accounting records to identify any possibility of GST evasion.
So, before rushing on all the minute areas which are covered under the GST audit. Let us first pay more emphasis on important points which should not be neglected.
Important points to be checked in GST Audit
#1 Anti-profiteering rules
Before the implementation of GST, rumors were getting spread about the inflation in prices of goods and services after the launch of GST. Goods and Service tax was aimed to reduce double taxation.
Anti-profiteering rules were launched on 18th June 2016. The rules were made to protect the consumers from retailers who will not pass the benefit of a reduction in the tax rate to the ultimate consumers.
If there is any reduction in tax rate then the benefit of the reduction in tax rate must be passed upon to the consumers by reducing the prices.
#2 Blocked credit under GST- Section 17(5)

There is a list of goods and services which are blocked input credit under GST.
“Blocked Credit” here refers to the goods and services on which the input tax credit cannot be claimed by the taxpayers.
The benefit of ITC is not available for these goods and services. For instance: ITC on Food and Beverages, Construction of Immovable property.
Author Advice
When the GST was launched in the month of July 2017. Taxpayers were having no clarity over Input tax credit provisions and blocked credit was claimed by many companies.
So, auditors should check the GST returns of July- Sep thoroughly.
#3 Transition forms Tran1 and Tran 2
The transition forms Tran 1 and Tran 2 were launched to claim an Input Tax credit on old stock. Auditors should verify that the credit transferred to Tran 1 or Tran 2 was an eligible credit and Transition forms must be filled for each GSTIN separately.
#4 Job Work under GST and GST ITC 04
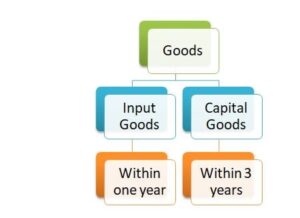
Under GST, the Delivery Challan format has been prescribed for the movement of goods from the principal to the job worker. Auditors should verify the appropriateness of Delivery Challans.
There are separate provisions for Input goods and Capital goods in Job work. Input goods must be returned within one year and Capital goods in three years.
What if goods are not returned in the specified time period? Then, it would be considered as “Deemed Supply” and tax will payable on such goods.
#5 Input Service Distributor and concept of Cross Billing
What is cross billing in GST?
Cross billing is applicable to the transactions between separate registrations of a single person. Whether the transactions should be considered as “supply”.GST applicability in the case of cross billing is a highly debatable topic.
Who is an Input Service Distributor?
It can be regarded as the office of the supplier of goods and services or both which received tax invoices towards receipt of input services and issues a document for the purpose of distributing the credit of GST to its branches.
Auditors should check whether the manner of distribution of credit by the Input service distributor specified under Section 20 and Rule 39 has been followed.
#6 RCM under GST
Although the list of services specified under Reverse Charge Mechanism in GST is similar to those of in Service tax law. But there are some services that need to be focused upon the auditor.
- Services through an e-commerce operator
- Import of services
- Services provided by way of sponsorship to any body corporate or partnership firm
- Services supplied by a director of a company or a body corporate to the said company or the body corporate
- Also, Auditors should focus upon ‘time of supply’ provisions in GST in the case of RCM services.
The above list is not exhaustive.
#7 Rule 37, Rule 42 &43 of CGST/SGST rules
Rule 37 deals with a reversal of GST of Input tax credit in case of nonpayment of consideration for the inward supply of goods and services within the prescribed limit.
Author advice: Auditors should perform an aging analysis of vendors to analyze the probable reasons for long outstanding vendors.
While Rule 42 and 43 deals with a reversal of Input tax credit attributable to making exempt supplies or for supplies meant for non-business use.
Auditors should thoroughly understand how ITC will be apportioned in Rule 42/43 before commencing any GST audit.
#8 Debit Notes and Credit Notes under GST
Debit Notes and Credit Notes are posing huge problems; Auditors are not able to reconcile Debit Note issued with Credit Note obtained. Some taxpayers have changed their policies of debiting the vendor. For example, Some are issuing Purchase return Notes, Debit Notes, or directly inflating the sales and Purchases.
Auditors should pay emphasis upon the procedure of issuing debit notes and credit notes and whether those are reflected in GST returns like GSTR-1 and GST 3B.
#9 Place of Supply in GST
The place of supply has also been a matter of concern for many taxpayers. Whether IGST will be levied or CGST/SGST, this has been a doubt for many taxpayers. Auditors should properly examine the provisions of Place of Supply in GST and should read the list of services on which different provisions are applicable.
#10 Import and Export in GST
How the companies are exporting under GST? Whether your client is paying IGST on supplies or exports are made through by issuing LUT? Check whether the IGST refund has been received by the taxpayer or did you checked the Notification Number of issuing LUT is mentioned upon the invoice.
Whether the Import and Export supplies have been reflected in GST return? What if any debit note is issued by the foreign customer? Whether GST number is mentioned upon Bill of Entry at the time of Import?
After analyzing the points of paramount importance, let us now jump upon the sample GST Audit checklist which can be used for conducting GST audits in an effective way.
Detailed GST Audit Checklist
Following the comprehensive GST Audit Checklist which can be used while conducting a GST audit.
- Obtain a list of all the GSTINs and addresses of the company at various locations.
- Check if any location in the same state is shown as an ‘additional place of business’
- Obtain a letter of undertaking in the current financial year, if the entity is an exporter.
- Compare the turnover of the entity in a current and previous financial year.
- List the HSN/SAC numbers used by the company for making any supplies.
- Checked whether there is any change in the tax rate on specified HSN and SAC.
- Is the GSTIN number displayed on the board at the main gate of the company?
- Is the GST registration certificate displayed at the prominent place of the business?
- Reconcile GSTR 1- and GST 3B
- Ascertain the reasons for the differences in reconciliation, if any
- Reconcile the accounting records with GSTR-1 & GST 3B
- Ascertain the reasons for any difference, if any
- Reconciliation above should be made separately for Outward Supplies and Input Tax Credit.
- Whether the ITC appearing in GST-3B reconciled with GST A by the management.
- If any difference in GST 3B and 2A has been observed, whether any communication has been made to the defaulter.
- What policy has been adopted by the company for persistent GST defaulters?
- Has the entity raised accounting debit notes to entities whose ITC is not appearing in GSTR-A?
- Ascertain the source of data in the Annual return. It should be accurate, with no chances of any error.
- Check whether GSTR is filled monthly or quarterly?
- Whether the returns are filed before the due date?
- Calculate the amount of Penalty or Interest levied in GST returns
- Check whether the same is matching with the amount mentioned in the Tax Audit report.
- Ascertain whether data has been prepared for GST ITC?
- If the entity is registered as a Composition Dealer, are GSTR- being filed on time? List dates of filing.
- Whether any GST registration was canceled?
- Check how inter-branch transfers are made to other states, using a tax invoice.
- Has the company sold any fixed assets? If yes, then GST would be levied if sold above written down value as per IT act,
- List all the transactions with the related parties. Whether the same rate is applied or different?
- Thoroughly examine the rate and HSN levied on ‘scrap sales’.
- In the case of a composite dealer, check whether ‘composite taxable person’ is mentioned upon the invoice.
- In the case of the composite supplier, no GST will be charged on the invoice, and only paid a percentage of sales
- GST Composition Supplier will mention his GSTIN and the fact of composition registration on the invoice
- Check whether the tax invoice is issued for rental and other incomes?
- Have bills of supply issued for exempt supplies?
- Check whether composite supplies have been taxed as per the rate applicable on the primary product?
- Check whether mixed supplies have been taxed at the highest rate applicable in the entire bundle of goods and services?
- Has the company deposited GST on advances?
- Ascertain whether the advances shown in returns have been adjusted in the subsequent period?
- Check whether the receipt note has been prepared for the advances.
- Ascertain the reason for issuing debit notes?
- Check whether an E-way bill for transportation of goods over Rs. was prepared if the material was rejected and a debit note was raised?
- Check whether a Credit note has been obtained for the corresponding debit note?
- Have GST Credit Notes been issued for a reduction in taxable value for invoices already issued?
- Examine the reason for issuing any credit note always.
- Check whether the proper effect of Debit notes and credit notes have been taken in GST return and accounting records.
- Have all the exports made without payment of tax under LUT?
- Check whether Notification No. is mentioned upon the invoice under LUT
- Check whether any export is made with payment of tax?
- Trace whether any refund on tax paid on export is pending or any case of litigation.
- Verify whether export sales have been shown correctly in GST return.
- Tax invoices under GST should always be serially numbered. Check whether they have been shown correctly in GST return?
- Interest at 18% p.a. is payable in case of short payment of output tax
- Interest at 24% p.a. is payable in case of a wrongful claim of the Input tax credit, which requires reversal.
- Check whether any late fees or interest is paid on the filing of GST returns.
- In the case of Job work, Input goods should be returned under one year.
- While Capital goods should be returned in under 3 years.
- In case goods are not returned within a specified time, it will be considered as deemed supply.
- Verify whether E-way bills are being prepared for the movement of goods.
- Check whether correct data is getting entered in E-way bills on a sample basis.
- Check whether IGST has been levied on Interstate sales and CGST/SGST on Intrastate sales.
- Verify whether all the vendors are properly charging IGST and CGST/SGST on inward supplies.
- Examine whether IGST has been levied on exports
- Have any supplies been made in relation to some fixed immovable property? Like architecture fees, accommodation services?
- Ascertain place of supply of goods is directly transferred to a third party?
- If goods are installed at a site, then the place of supply will the place where the goods are installed.
- If training is provided to an unregistered person, the place of supply is the place where such services are performed.
- Check the place of supply, in case of a supply of goods requiring any movement?
- If training is provided to the registered person, the place of supply is the place where the recipient is registered.
- Check whether GST has been charged on the gross value of freight, other charges?
- If any interest/penalty has been recovered for delayed payment, then whether GST has been levied on such payment.
- Has discount separately shown upon the invoice
- After-sale discounts must be reduced from the taxable value by issuing a credit note. GST should be levied on that.
- Has a proper ledger has been maintained in accounting records for separate recording of IGST, SGST, and CGST?
- Check whether ITC has been claimed on goods imported in India and IGST has been charged on custom duty?
- Check whether GST has been paid on RCM services?
- Examine the RCM invoice made. It should be as per the format prescribed under GST.
- Has a payment voucher been made for all such payments covered under RCM?
- The reverse charge should be paid in Cash not by utilizing any ITC in an electronic credit ledger.
- Check whether ITC credit has been claimed on RCM invoices in subsequent months?
- Has TDS been deducted by the government recipient on payment being made to the entity? If yes, is the credit being taken in each GSTR-B as per GSTR-A?
- Check whether any credit will be reversed under Section 17(5), whether interest has been paid on reversal.
- Verify whether all the conditioned mention in Section to claim ITC have complied.
- Check whether Credit has been apportioned under Rule /.
- Perform an aging analysis of creditors to trace the credit which needs to be reversed under Rule.
- Check whether the GSTIN of both supplier and customer has been mentioned upon the invoice.
- Manner of adjusting Input tax credit has been changed quite a few times. Check the appropriate law prevalent at that time.
- If the goods are received in the lot, ITC will be claimed on the last installment.
- Obtain copies of GST notice received from authorities and corresponding replies made.
- Check the status of demand based on the notice sent by the department.
- In case of any GST search; check whether proper actions have been taken to avoid any subsequent penalties.
- Has the company applied for any advance ruling, If yes details thereof?
- Check If any reduction in the tax rate, benefit in reduction has been transferred to the customer by mitigating price.
- Obtain copies of past orders under previous indirect taxes such as VAT, Service Tax, and Excise to examine corresponding GST compliance.
- Examine the time of supply provisions.
- Determine the time of supply in case of a change in the rate of tax
- Check the exclusions and inclusions in the value of supply mentioned under Section
- The accounting records should be preserved for months from the due date furnishing the annual return for the year to which it relates.
Copy the above GST audit checklist and take a print out to conduct the Audit efficently. You can mark Yes/No or provide any remarks along with the points.

Connect with us at +917701879108 and gstmentor1@gmail.com