Page Contents
Audit Procedures for Inventory and making a Stock Audit Checklist
In this article, we will learn about audit procedures for inventory and how we can prepare a stock audit checklist by understanding the environment of the entity and audit techniques to be levied. Auditing is a dynamic concept, we cannot use the same checklist for each and every client.
Every client operates in a different environment. So, instead of downloading a fixed checklist. Learn to develop it on your own knowledge. We will go through the inventory processes in a company, and at each stage, we will learn about the risk associated and audit procedures to be levied.
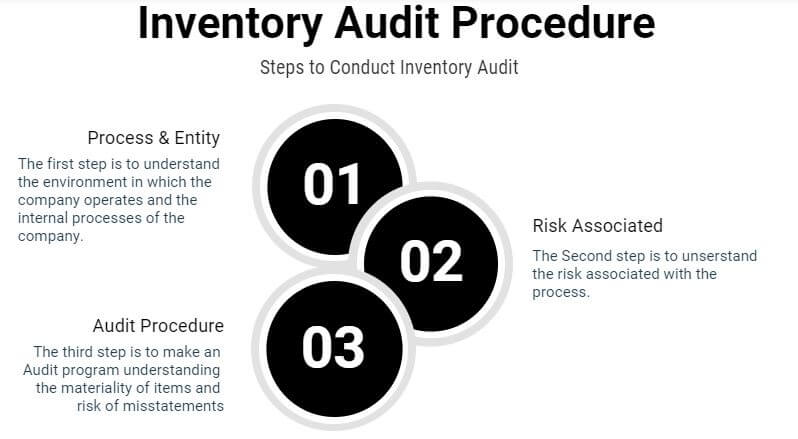
So, we categorize the whole blog post into three stages.
Stage 1 Understanding the Process of the company
Stage 2 Risk associated with the process
Stage 3 Designing the Audit procedures
Beginning with our first process.
Always remember assertions In Inventory Audit – ” Existence” and “Condition”.
Read about Purchase Process Auditing Procedure
Reconciliation of material lying at the plant or with the third party
The first and foremost process management should undertake is to reconcile the material lying at the factory with the inventory records. Most of the factories outsource some process like electroplating which we call job work. The goods sent on job work must be received within the prescribed time.
Risk Associated with the process.
What are the various risks associated if material reconciliation is not prepared by the management? We will discuss each and every one.
- The first and foremost issue is the over-valuation of inventory in the accounting records than it is physically available. Management should prepare reconciliation periodically by conducting physical verification at periodic intervals.
- Understanding the usage of material, excess usage than standard requirements can result in financial losses.
- Non-compliance with the agreement entered into with the job workers.
- There is a possibility of a loss of material sent on job work.
- It can also happen that material is received back from the job worker, however not recorded in ERP system.
- Input Tax credit needs to be reversed for the Input and Capital goods if not received within time.
Audit Procedures to be levied
How Auditors should implement their procedures while ascertaining the existence and condition of inventory?
- First, obtain a month-wise material reconciliation report. The normal frequency is one month, in some companies physical verification is quarterly also. On a sample basis, stock can be physically verified by the auditors also.
- Auditors should identify variances between stock as per ERP (Accounting Records) and physical count.
- Examine principles or norms on which reconciliation is prepared for finished, work in progress, and raw inventory.
- Check whether there is any revision of norms and procedures and whether updated norms are used in the preparation of material reconciliation. And in case of any deviation report it to the appropriate authority.
- Check for the accuracy, completeness, and correctness of the Material Reconciliation prepared as such.
- For dealing with the third parties like job workers, the first step auditor should obtain the contract entered with job workers and check whether the terms as agreed in the contract have been complied with.
- Check whether GST credit has been reversed in respect of input goods pending to be received for more than 1 year and 3 years in the case of capital goods).
- Check Delivery Challans for completeness and accuracy of data recording. Also, check whether an E-way bill has been issued for them. E-way Bill is mandatory for Job work in India.
- Reconciled the balance as per ERP and goods lying with the job worker and at the factory premises.
- There might be normal loss associated with the job work process. Identify the variances in actual scrapped quantity received from the job work process with the standard consumption.
Moving on to the second process.
Identifying Slow or Non-Moving Inventory Items (Important for Stock Audit Checklist)
Why there is a need to identify slow or non-moving items. Use your analytical mind, Why? The slow-moving items increase the inventory carrying cost plus get obsolete over time. What we can do for them? We can establish just in time purchasing system for those goods.
Risks Associated with slow-moving inventory
- Slow-moving inventory is not correctly identified which results in blockage of Working capital.
- Excess or Short holding results due to not defining inventory norms.
- Accounting of Non Moving or Slow Inventory should be according to the Accounting Standards.
- Obsolete items are written off from accounting records without authorization.
Audit procedures to be levied
Like Management, Auditor should first identify the slow-moving items then apply other audit procedures or techniques.
- Extract inventory aging report from the ERP system (if possible) having details of slow-moving, non-moving & obsolete inventory.
- Identify categories of inventory that are slow-moving with the defined Inventory movement norms.
- Understand the principles over which Inventory movement norms are defined. Check their approval by sanctioning authority, any amendments or modifications made to them by the supplier or concerned person.
- Conduct physical verification of sample obsolete items, and check their treatment in accounting records.
- Discuss and understand the policy of identifying inventory to be written off from the above list. Inventory should be written off without the approval of the appropriate authority.
- Check GST provisions on the write-off of stock.
- Understand how management reached the level of ideal stock for the production line and find out if such a basis needs revision.
The next one is easy to understand but difficult to implement.
Reviewing the production losses occurring on account of delay in material received from supplier or job worker.
There are instances when the material is not received on time from the supplier. This results in production losses to the company, the nonavailability of material increases the idle time. This is the primary reason why large manufacturing companies have a long process of selecting the job worker or supplier.
Read about Vendor Selection Procedure
Understanding the Risk Associated
- The first and foremost is companies don’t have any scientific method of recording production losses. Production losses are often ignored like they never happened. The reason they are ignored as the person causing the loss would directly come to light.
- Recurrence of avoidable production losses.
- Production Loss accounting in the accounting records. Would accounting standards allow?
Audit Procedures
As I said it is going to be a little tough to identify and understand how production losses are actually happening. You need Costing knowledge to allocate the abnormal losses.
- First, we need to understand how the company captures and monitors production losses.
- If available obtain or prepare day-wise and month-wise loss time reports.
- The next step would be to quantify the loss. Material Quantification would result in direct reporting to the appropriate person.
- Ensure whether the reason for production losses is rightly allocated to each production process.
- Accounting treatment of production losses is the area of concern. Check whether abnormal overheads are not getting capitalized in the books.
- Calculate Overall Equipment Effectiveness. The availability ratio would definitely be impacted.
- Identify the reason for the delay in material from the job worker.
Accounting when the material journal entry is directly entered into the system
Instances where an accounting entry is directly passed into the system without particularly defining each and every item. However, most of the ERP’s don’t allow recording in such a way but old ERP’s like Tally would allow.
Risk Associated
- The first risk would be overvaluation or it would result in undervaluation of inventory than the physical value.
- Management can act in collusion and pass unauthorized entries by inflating the inventory records.
- Issues that led to passing such entry would never be identified and such issues might recur.
- Passing a backdated journal without permission
Audit Procedures
- First, we need to how these inventory adjustments are getting passed.
- Check whether requisite approval has been obtained for doing such adjustments.
- Identify the root cause of why such a journal is passed. Prepare an inventory adjustment summary by combining such journals.
- Analyze the summary prepared and identify entries that are pending adjustment.
- Ascertain who has access controls to pass backdated entries.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Inventory audit questionnaire, plan or program can be designed using the above mentioned audit procedures. We can classify the process we are going to audit and then add on our audit procedure points.
We have discussed the risk associated above. The risk associated would become the base on which internal controls should be designed. This will mitigate the risks of any material misstatement.